Lab 7A/7B: Rotary Encoder (Week 11-12)
Overview
In this lab, you will interface with a rotary encoder - a common input device that converts rotational motion into digital signals. You will design a state machine to decode the rotation direction and create an up/down counter controlled by the encoder.
Learning Objectives
After completing this lab, you will be able to:
- Understand rotary encoder operation (quadrature encoding)
- Implement debouncing for mechanical switches
- Design a Finite State Machine (FSM) to decode rotation
- Create an up/down counter controlled by the encoder
- Apply state machines to real-world interfacing problems
Background: Rotary Encoder
What is a Rotary Encoder?
A rotary encoder is an electro-mechanical device that converts angular position or rotation to digital signals. It outputs two square waves (A and B) that are 90° out of phase (quadrature signals).
Quadrature Encoding
The phase relationship between signals A and B indicates rotation direction:
Clockwise Rotation:
A: ─┐ ┌─┐ ┌─┐ ┌─
└─┘ └─┘ └─┘
B: ──┐ ┌─┐ ┌─┐ ┌
└─┘ └─┘ └─┘
(A leads B by 90°)
Counter-Clockwise:
A: ──┐ ┌─┐ ┌─┐ ┌
└─┘ └─┘ └─┘
B: ─┐ ┌─┐ ┌─┐ ┌─
└─┘ └─┘ └─┘
(B leads A by 90°)
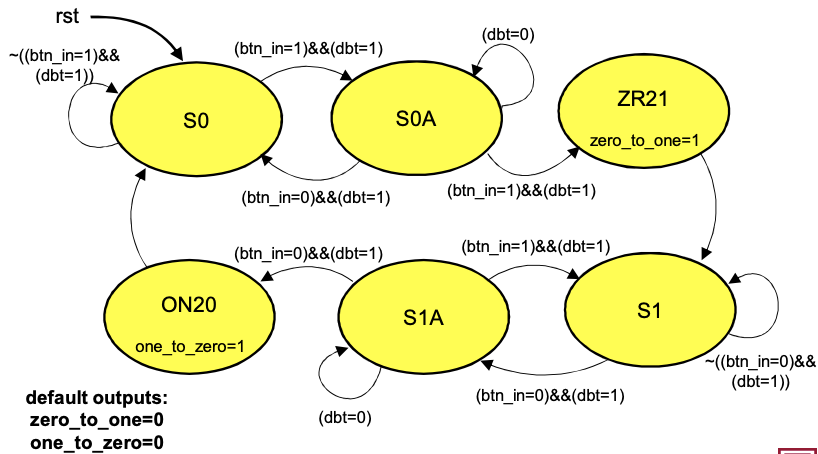
Figure 1: Rotary Encoder Quadrature State Machine
State Transitions
| Current State (A,B) | Next State (A,B) | Direction |
|---|---|---|
| 00 → 01 | Clockwise | |
| 01 → 11 | Clockwise | |
| 11 → 10 | Clockwise | |
| 10 → 00 | Clockwise | |
| 00 → 10 | Counter-Clockwise | |
| 10 → 11 | Counter-Clockwise | |
| 11 → 01 | Counter-Clockwise | |
| 01 → 00 | Counter-Clockwise |
Design: Debouncing
Why Debounce?
Mechanical contacts in encoders cause contact bounce - rapid oscillations between 0 and 1 when the contact changes state. This can cause false state transitions.
Debounce Circuit
module debounce #(
parameter DEBOUNCE_TIME = 50000 // Clock cycles (~1ms at 50MHz)
)(
input logic clk,
input logic rst_n,
input logic noisy, // Raw input from encoder
output logic clean // Debounced output
);
logic [15:0] counter;
logic sync_in, prev_in;
// Synchronizer (2-stage for metastability)
always_ff @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
sync_in <= 1'b0;
prev_in <= 1'b0;
end else begin
sync_in <= noisy;
prev_in <= sync_in;
end
end
// Debounce counter
always_ff @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
counter <= '0;
clean <= 1'b0;
end else if (prev_in != clean) begin
// Input different from stable output
if (counter == DEBOUNCE_TIME - 1) begin
clean <= prev_in;
counter <= '0;
end else begin
counter <= counter + 1'b1;
end
end else begin
counter <= '0;
end
end
endmodule
Design: Quadrature Decoder FSM
State Machine Approach
module quadrature_decoder (
input logic clk,
input logic rst_n,
input logic a_in, // Encoder A (debounced)
input logic b_in, // Encoder B (debounced)
output logic cw_pulse, // Clockwise rotation pulse
output logic ccw_pulse // Counter-clockwise rotation pulse
);
// State encoding: {prev_a, prev_b}
logic [1:0] prev_state, curr_state;
assign curr_state = {a_in, b_in};
always_ff @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
prev_state <= 2'b00;
cw_pulse <= 1'b0;
ccw_pulse <= 1'b0;
end else begin
prev_state <= curr_state;
// Detect transitions
case ({prev_state, curr_state})
// Clockwise: 00→01→11→10→00
4'b00_01: begin cw_pulse <= 1'b1; ccw_pulse <= 1'b0; end
4'b01_11: begin cw_pulse <= 1'b1; ccw_pulse <= 1'b0; end
4'b11_10: begin cw_pulse <= 1'b1; ccw_pulse <= 1'b0; end
4'b10_00: begin cw_pulse <= 1'b1; ccw_pulse <= 1'b0; end
// Counter-clockwise: 00→10→11→01→00
4'b00_10: begin cw_pulse <= 1'b0; ccw_pulse <= 1'b1; end
4'b10_11: begin cw_pulse <= 1'b0; ccw_pulse <= 1'b1; end
4'b11_01: begin cw_pulse <= 1'b0; ccw_pulse <= 1'b1; end
4'b01_00: begin cw_pulse <= 1'b0; ccw_pulse <= 1'b1; end
default: begin cw_pulse <= 1'b0; ccw_pulse <= 1'b0; end
endcase
end
end
endmodule
Design: Rotation Counter
module rotation_counter #(
parameter WIDTH = 16
)(
input logic clk,
input logic rst_n,
input logic cw_pulse, // Clockwise
input logic ccw_pulse, // Counter-clockwise
output logic [WIDTH-1:0] count
);
always_ff @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n)
count <= '0;
else if (cw_pulse)
count <= count + 1'b1;
else if (ccw_pulse)
count <= count - 1'b1;
end
endmodule
Complete System Integration
Figure 2: Complete Rotary Encoder System Block Diagram
Top-Level Module
module lab7_top (
input logic MAX10_CLK1_50,
input logic [9:0] SW,
input logic [1:0] KEY,
input logic [35:0] GPIO, // GPIO for encoder
output logic [9:0] LEDR,
output logic [6:0] HEX0,
output logic [6:0] HEX1,
output logic [6:0] HEX2,
output logic [6:0] HEX3
);
logic clk, rst_n;
logic enc_a_raw, enc_b_raw;
logic enc_a, enc_b;
logic cw_pulse, ccw_pulse;
logic [15:0] count;
assign clk = MAX10_CLK1_50;
assign rst_n = KEY[0];
// Encoder inputs from GPIO
assign enc_a_raw = GPIO[0];
assign enc_b_raw = GPIO[1];
// Debounce both encoder signals
debounce u_deb_a (
.clk(clk), .rst_n(rst_n),
.noisy(enc_a_raw), .clean(enc_a)
);
debounce u_deb_b (
.clk(clk), .rst_n(rst_n),
.noisy(enc_b_raw), .clean(enc_b)
);
// Decode quadrature signals
quadrature_decoder u_decoder (
.clk(clk), .rst_n(rst_n),
.a_in(enc_a), .b_in(enc_b),
.cw_pulse(cw_pulse), .ccw_pulse(ccw_pulse)
);
// Up/Down counter
rotation_counter u_counter (
.clk(clk), .rst_n(rst_n),
.cw_pulse(cw_pulse), .ccw_pulse(ccw_pulse),
.count(count)
);
// Display count on 7-segment displays
svn_seg_decoder u_h0 (.bcd_in(count[3:0]), .display_on(1'b1), .seg_out(HEX0));
svn_seg_decoder u_h1 (.bcd_in(count[7:4]), .display_on(1'b1), .seg_out(HEX1));
svn_seg_decoder u_h2 (.bcd_in(count[11:8]), .display_on(1'b1), .seg_out(HEX2));
svn_seg_decoder u_h3 (.bcd_in(count[15:12]), .display_on(1'b1), .seg_out(HEX3));
// Show direction on LEDs
assign LEDR[0] = cw_pulse;
assign LEDR[1] = ccw_pulse;
assign LEDR[9:2] = 8'b0;
endmodule
Hardware Connections
Connect the rotary encoder to the DE10-Lite GPIO:
| Encoder Pin | GPIO Pin | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A | GPIO[0] | Encoder signal A |
| B | GPIO[1] | Encoder signal B |
| GND | GND | Ground |
| VCC | 3.3V | Power supply |
Verification
Simulation Testbench
module quadrature_decoder_tb;
logic clk, rst_n;
logic a_in, b_in;
logic cw_pulse, ccw_pulse;
quadrature_decoder uut (.*);
initial clk = 0;
always #10 clk = ~clk;
initial begin
rst_n = 0; a_in = 0; b_in = 0;
#50 rst_n = 1;
// Simulate clockwise rotation
$display("Clockwise rotation:");
a_in = 0; b_in = 0; #100;
a_in = 0; b_in = 1; #100;
a_in = 1; b_in = 1; #100;
a_in = 1; b_in = 0; #100;
a_in = 0; b_in = 0; #100;
// Simulate counter-clockwise rotation
$display("Counter-clockwise rotation:");
a_in = 0; b_in = 0; #100;
a_in = 1; b_in = 0; #100;
a_in = 1; b_in = 1; #100;
a_in = 0; b_in = 1; #100;
a_in = 0; b_in = 0; #100;
$finish;
end
endmodule
Lab Manual
📄 Download Lab 7A/7B Manual (PDF)
Deliverables
- SystemVerilog Design:
debounce.sv,quadrature_decoder.sv,rotation_counter.sv,lab7_top.sv - State Diagram: Draw FSM for quadrature decoding
- Testbench: Verify CW and CCW detection
- Hardware Demo: Count up/down with encoder rotation
- Individual Screenshots: Simulation waveforms
- Submission: Upload
lab7b_top.svffile
Applications
- Volume controls (audio equipment)
- Menu navigation (appliances, instruments)
- Position sensing (robotics, CNC machines)
- Scroll wheels (computer mice)